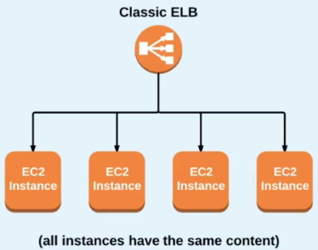
Classic ELB:
- makes routing decisions at either the transport layer (TCP/SSL) or the application layer (HTTP/HTTPs), and supports either EC2-Classic or a VPC.
- A "Classic" ELB is designed for simple balancing of traffic to multiple EC2 instances.
- There are no granular routing "rules" - all instances get routed to evenly, and no special routing request can be made based on specific content request from the user.
Classic load balancing is best used when all instances (that are being served traffic) contain the same data.
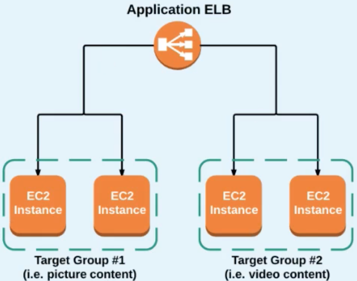
Application ELB:
makes routing decisions at the application layer (HTTP/HTTPs), supports path-based routing, and can route requests to one or more ports on each EC2 instance or container instance in your VPC.
An "application" ELB is designed for complex balancing of traffic to multiple EC2 instances using Content-based "rules".
Content-based rules (setup on the listener) can be configured using:
Host-based rules: Route traffic based on the host field of the HTTP header.
Path-based rules: Route traffic based on the URL path of the HTTP header.
This allows you to structure your application as smaller services, and even monitor/auto-scale based on traffic to specific "target-groups".
An application ELB also supports ECS container, HTTPS, HTTP/2, Web Sockets, Access Logs, Sticky Sessions, and AWS AWF (Web Application Firewall).